12.其他库的介绍
为什么需要哈希函数?
哈希函数在计算机科学中扮演着重要的角色,其主要作用包括:
-
数据检索:哈希函数可以将键(key)映射到哈希表中的一个位置,从而快速检索数据。这是哈希表(如 C++ 中的
std::unordered_map和std::unordered_set)的基础。 -
快速比较:在数据库和各种数据结构中,哈希函数可以快速比较字符串或对象,常用于检查两个字符串是否相等。
-
数据分布:在分布式系统中,哈希函数可以将数据均匀地分布到多个节点上,以实现负载均衡。
-
密码学应用:在密码学中,哈希函数用于生成数据的摘要,用于数据完整性验证和数字签名。
-
缓存实现:哈希函数可以用于实现缓存机制,通过快速定位缓存中的数据。
-
负载均衡:在网络流量管理中,哈希函数可以用于将请求分配到不同的服务器上。
C++ 库中哈希函数的实现和底层逻辑
在 C++11 及以后的版本中,标准库提供了一个专门的哈希函数库 <functional>,其中包含了 std::hash 模板类。std::hash 为基本数据类型(如 int、double、std::string 等)提供了特化版本。
实现底层逻辑:
-
整数类型:对于整数类型,
std::hash直接返回数值本身或其变体。例如,对于int类型,std::hash<int>()(10)可能直接返回 10 或者 10 的一个简单变换。 -
浮点类型:对于浮点类型,
std::hash通常会将浮点数的位表示转换为整数,然后应用整数的哈希函数。 -
字符串类型:对于字符串,
std::hash通常会遍历字符串中的每个字符,将每个字符的哈希值组合起来,生成最终的哈希值。这可以通过位操作和数学函数(如乘法、加法、异或等)来实现。 -
自定义类型:对于自定义类型,如果需要使用
std::hash,则需要为该类型提供自定义的哈希函数。 -
组合哈希:对于复合类型(如结构体或类),哈希函数需要将各个成员的哈希值组合起来。这通常通过将成员的哈希值进行某种形式的数学运算(如加权求和、异或等)来实现。
-
均匀分布:一个好的哈希函数应该能够产生均匀分布的哈希值,以减少哈希冲突。
-
确定性:哈希函数应该是确定性的,即对于同一个输入总是产生相同的哈希值。
-
快速计算:哈希函数的计算应该尽可能快,以减少对性能的影响。
在 C++ 中,std::hash 的实现可能因编译器和平台而异,但基本原理是相似的。正确实现哈希函数对于哈希表的性能至关重要,因为它直接影响到哈希表的冲突率和检索效率。
hash function-哈希函数
如果要自己给自己的数据写一个哈希函数,那又该怎么写呢?能否基于这些数据计算出hash code的呢?
编写模版规范
#include <functional>
namespace test_hash_function
{
class Customer {
private:
string fname;
string lname;
int on;
public:
Customer( string fn, string ln, int id) : fname(fn), lname(ln), on(id) {}
bool operator==(const Customer& other) const {//需要重载==
return fname == other.fname && lname == other.lname && on == other.on;
}
friend class CustomerHash;
};
class CustomerHash {
public:
std::size_t operator()(const Customer& c) const {
return ...;
}
};
unordered_set<Customer, CustromerHash> custsct;
} #include <functional>
namespace test_hash_function
{
template <typename T>
inline void hash_combine(size_t& seed, const T& val) {
seed ^= hash<T>()(val) +
0x9e3779b9 +
(seed << 6) +
(seed >> 2);
}
template <typename T>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val) {
hash_combine(seed, val);
}
template <typename T, typename... Types>
inline void hash_val( size_t& seed,
const T& val,
const Types&... args)
{
hash_combine(seed, val);
hash_val(seed, args...);
}
template <typename... Types>
inline size_t hash_val(const Types&... args) {
size_t seed = 0;
hash_val(seed, args...);
return seed;
}
class Customer {
private:
string fname;
string lname;
int on;
public:
Customer( string fn, string ln, int id) : fname(fn), lname(ln), on(id) {}
bool operator==(const Customer& other) const {
return fname == other.fname && lname == other.lname && on == other.on;
}
friend class CustomerHash;
};
class CustomerHash {
public:
size_t operator()(const Customer& c) const {
return hash_val(c.fname, c.lname, c.on);
}
};
void test() {
unordered_set<Customer, CustomerHash> s;
s.insert(Customer("Asd", "dfw", 1L));
s.insert(Customer("Dfg", "kjt", 2L));
s.insert(Customer("VVB", "ert", 3L));
s.insert(Customer("TgR", "uik", 4L));
s.insert(Customer("Gdf", "pii", 5L));
s.insert(Customer("Gdf", "pii", 6L));
s.insert(Customer("Gdf", "pii", 7L));//8
cout << s.bucket_count() << endl;
CustomerHash hh;
cout << hh(Customer("Asd", "dfw", 1L)) % 8 << endl;//4
cout << hh(Customer("Dfg", "kjt", 2L)) % 8 << endl;//0
cout << hh(Customer("VVB", "ert", 3L)) % 8 << endl;//3
cout << hh(Customer("TgR", "uik", 4L)) % 8 << endl;//7
cout << hh(Customer("Gdf", "pii", 5L)) % 8 << endl;//2
cout << hh(Customer("Gdf", "pii", 6L)) % 8 << endl;//7
cout << hh(Customer("Gdf", "pii", 7L)) % 8 << endl;//4
for (unsigned i = 0; i < s.bucket_count(); i++) {
cout << "bucked #" << i << "has" << s.bucket_size(i) << "element\n";
}
}
}
// bucked #0has1element
// bucked #1has0element
// bucked #2has1element
// bucked #3has1element
// bucked #4has2element
// bucked #5has0element
// bucked #6has0element
// bucked #7has2element
#include <functional>
namespace test_hash_function
{
class Customer {
private:
string fname;
string lname;
int on;
public:
Customer( string fn, string ln, int id) : fname(fn), lname(ln), on(id) {}
bool operator==(const Customer& other) const {//需要重载==
return fname == other.fname && lname == other.lname && on == other.on;
}
friend class CustomerHash;
};
class CustomerHash {
public:
size_t customer_hash_func(const Customer& c) const {
return ...;
}
};
unordered_set<Customer, size_t(*)(const Custromer&)> custsct(20,customer_hash_func);//注意与类型1的不同写法
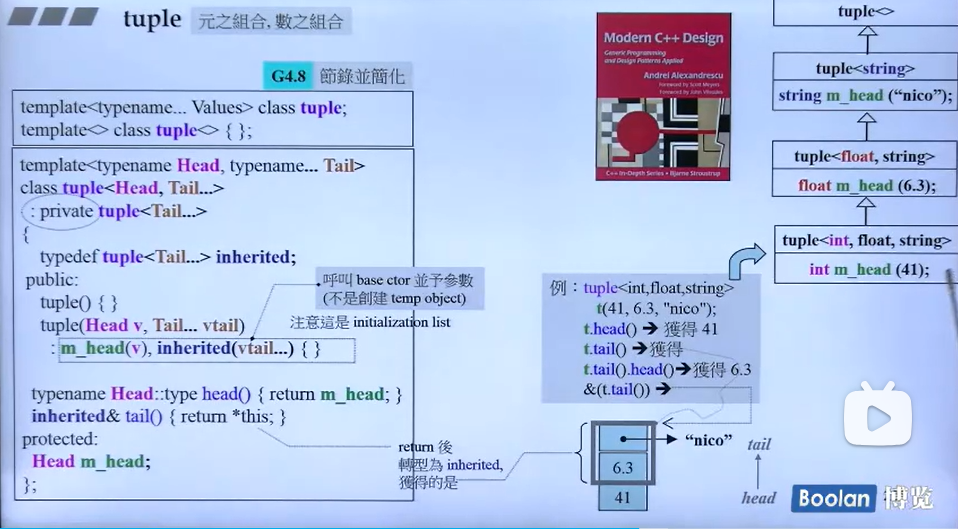
}tuple
在C++中,tuple 是一个标准库模板类,它提供了一种方式来存储不同类型数据的集合。tuple 类似于一个固定大小的数组,但是数组中的每个元素可以是不同的类型。这个特性使得 tuple 非常灵活,可以用于多种场景。